松哥周末抽空给 Spring Security 系列也录制了一套视频,目录如下:

感兴趣的小伙伴戳这里-->Spring Boot+Vue+微人事视频教程
来看今天的文章。
前面松哥发过两篇文章,也是两种方案,讲到单点登录问题:
今天再来和大家介绍第三种方案,使用 Spring Security 开发 CAS 单点登录系统客户端。
上篇文章讲了 CAS 单点登录以及 CAS Server 的搭建问题,CAS Server 搭建好了,接下来我们要搭建具体的应用,本文我们就来看看 Spring Security+CAS 如何实现单点登录。
本文在上篇文章的基础上继续完成,如果小伙伴们的 CAS Server 还没搭建成功,可以参考上篇文章。
本文是 Spring Security 系列第 24 篇,阅读本系列前面文章有助于更好的理解本文:
- 挖一个大坑,Spring Security 开搞!
- 松哥手把手带你入门 Spring Security,别再问密码怎么解密了
- 手把手教你定制 Spring Security 中的表单登录
- Spring Security 做前后端分离,咱就别做页面跳转了!统统 JSON 交互
- Spring Security 中的授权操作原来这么简单
- Spring Security 如何将用户数据存入数据库?
- Spring Security+Spring Data Jpa 强强联手,安全管理只有更简单!
- Spring Boot + Spring Security 实现自动登录功能
- Spring Boot 自动登录,安全风险要怎么控制?
- 在微服务项目中,Spring Security 比 Shiro 强在哪?
- SpringSecurity 自定义认证逻辑的两种方式(高级玩法)
- Spring Security 中如何快速查看登录用户 IP 地址等信息?
- Spring Security 自动踢掉前一个登录用户,一个配置搞定!
- Spring Boot + Vue 前后端分离项目,如何踢掉已登录用户?
- Spring Security 自带防火墙!你都不知道自己的系统有多安全!
- 什么是会话固定攻击?Spring Boot 中要如何防御会话固定攻击?
- 集群化部署,Spring Security 要如何处理 session 共享?
- 松哥手把手教你在 SpringBoot 中防御 CSRF 攻击!so easy!
- 要学就学透彻!Spring Security 中 CSRF 防御源码解析
- Spring Boot 中密码加密的两种姿势!
- Spring Security 要怎么学?为什么一定要成体系的学习?
- Spring Security 两种资源放行策略,千万别用错了!
- 聊一聊 Spring Boot 中的 CAS 单点登录
# 1.准备工作
准备工作主要做两件事。
# 1.1 服务记录
某一个 Client 需要接入 CAS Server 进行验证,则该 Client 必须提前在 CAS Server 上配置其信息。
这个信息既可以动态添加,也可以通过 JSON 来配置,后面松哥会教搭建如何动态添加,这里方便起见,我们还是通过 JSON 来进行配置。
具体配置方式如下,在 CAS Server 中创建如下目录:
src/main/resources/services
在该目录下创建一个名为 client1-99.json 的文件,client1 表示要接入的 client 的名字,99 表示要接入的 client 的 id,json 文件内容如下(这个配置可以参考官方给出的模版:overlays/org.apereo.cas.cas-server-webapp-tomcat-5.3.14/WEB-INF/classes/services/Apereo-10000002.json):
{
"@class": "org.apereo.cas.services.RegexRegisteredService",
"serviceId": "^(https|http)://.*",
"name": "client1",
"id": 99,
"description": "应用1 的定义信息",
"evaluationOrder": 1
}
这段 JSON 配置含义如下:
- @calss 指定注册服务类,这个是固定的org.apereo.cas.services.RegexRegisteredService。
- serviceId 则通过正则表达式用来匹配具体的请求。
- name 是接入的 client 的名称。
- id 是接入的 client 的 id。
- description 是接入的 client 的描述信息。
- evaluationOrder 则指定了执行的优先级。
接下来再在 src/main/resources/application.properties 文件中配置刚刚 json 的信息,如下:
cas.serviceRegistry.json.location=classpath:/services
cas.serviceRegistry.initFromJson=true
这里有两行配置:
- 指定配置 JSON 文件的位置。
- 开启 JSON 识别。
OK,配置完成后,重启 CAS Server。
CAS Server 启动成功后,我们在控制台看到如下日志,表示 JSON 配置已经加载成功了:

# 1.2 JDK 证书
第二个要提前准备的东西就是 JDK 证书。
在实际开发中,这一步可以忽略,但是因为我们现在用的自己生成的 SSL 证书,所以我们要将自己生成的证书导入到 JDK 中,否则在使用 Spring Security 接入 CAS 单点登录时,会抛出如下错误:

将 SSL 证书导入 JDK 中的命令其实也很简单,两个步骤,第一个导出 .cer 文件,第二步,导入 JDK,命令如下:
keytool -export -trustcacerts -alias casserver -file ./cas.cer -keystore ./keystore
sudo keytool -import -trustcacerts -alias casserver -file ./cas.cer -keystore /Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk-10.0.2.jdk/Contents/Home/lib/security/cacerts
注意,在执行 export 导出命令时,需要输入密钥口令,这个口令就是自己一开始创建 SSL 证书时设置的。在执行 import 导入命令时,也需要输入口令,这个口令是 changeit,注意,不是自己一开始设置的。
密钥库的位置在 JDK 目录下的 /lib/security/cacerts,小伙伴们根据自己实际情况来修改(在 JDK9 之前,位置在 jre/lib/security/cacerts)。
我们在本地测试一定要导入证书到 JDK 证书库中,否则后面的测试会出现上图中的错误,证书导入 JDK 证书库之后,要确保之后的开发中,使用的是本地的 JDK。
注意,JDK 证书导入之后,CASServer 需要重启一下。
# 1.3 修改 hosts
另外,我们还需要修改电脑 hosts 文件,因为前面关于 CAS Server,关于 SSL 证书的配置都涉及到域名,所以后面的访问我们将通过域名的形式访问,hosts 文件中添加如下两条记录:
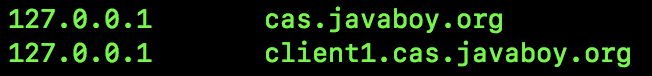
第一个是 CAS Server 的请求域名,第二个是 CAS Client 的请求域名。
# 2.开发 Client
在使用 Spring Security 开发 CAS Client 之前,有一个基本问题需要先和小伙伴们捋清楚:用户登录是在 CAS Server 上登录,所以 Spring Security 中虽然依旧存在用户的概念,但是对于用户的处理逻辑会和前面的有所不同。
好了,接下来我们来看下具体步骤。
首先我们来创建一个普通的 Spring Boot 项目,加入 Web 依赖 和 Spring Security 依赖,如下:
项目创建成功后,我们再来手动加入 cas 依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-security-cas</artifactId>
</dependency>
接下来,在 application.properties 中配置 CAS Server 和 CAS Client 的请求地址信息:
cas.server.prefix=https://cas.javaboy.org:8443/cas
cas.server.login=${cas.server.prefix}/login
cas.server.logout=${cas.server.prefix}/logout
cas.client.prefix=http://client1.cas.javaboy.org:8080
cas.client.login=${cas.client.prefix}/login/cas
cas.client.logoutRelative=/logout/cas
cas.client.logout=${cas.client.prefix}${cas.client.logoutRelative}
这些配置都是自定义配置,所以配置的 key 可以自己随意定义。至于配置的含义都好理解,分别配置了 CAS Server 和 CAS Client 的登录和注销地址。
配置好之后,我们需要将这些配置注入到实体类中使用,这里就用到了类型安全的属性绑定(参见:Spring Boot2 系列教程(四)理解配置文件 application.properties !)。
这里我创建两个类分别用来接收 CAS Server 和 CAS Client 的配置文件:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "cas.server")
public class CASServerProperties {
private String prefix;
private String login;
private String logout;
//省略 getter/setter
}
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "cas.client")
public class CASClientProperties {
private String prefix;
private String login;
private String logoutRelative;
private String logout;
//省略 getter/setter
}
另外记得在启动类上面添加 @ConfigurationPropertiesScan 注解来扫描这两个配置类:
@SpringBootApplication
@ConfigurationPropertiesScan
public class Client1Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Client1Application.class, args);
}
}
这里配置完成后,我们一会将在配置文件中来使用。
接下来创建 CAS 的配置文件,略长:
@Configuration
public class CasSecurityConfig {
@Autowired
CASClientProperties casClientProperties;
@Autowired
CASServerProperties casServerProperties;
@Autowired
UserDetailsService userDetailService;
@Bean
ServiceProperties serviceProperties() {
ServiceProperties serviceProperties = new ServiceProperties();
serviceProperties.setService(casClientProperties.getLogin());
return serviceProperties;
}
@Bean
@Primary
AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint() {
CasAuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = new CasAuthenticationEntryPoint();
entryPoint.setLoginUrl(casServerProperties.getLogin());
entryPoint.setServiceProperties(serviceProperties());
return entryPoint;
}
@Bean
TicketValidator ticketValidator() {
return new Cas20ProxyTicketValidator(casServerProperties.getPrefix());
}
@Bean
CasAuthenticationProvider casAuthenticationProvider() {
CasAuthenticationProvider provider = new CasAuthenticationProvider();
provider.setServiceProperties(serviceProperties());
provider.setTicketValidator(ticketValidator());
provider.setUserDetailsService(userDetailService);
provider.setKey("javaboy");
return provider;
}
@Bean
CasAuthenticationFilter casAuthenticationFilter(AuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider) {
CasAuthenticationFilter filter = new CasAuthenticationFilter();
filter.setServiceProperties(serviceProperties());
filter.setAuthenticationManager(new ProviderManager(authenticationProvider));
return filter;
}
@Bean
SingleSignOutFilter singleSignOutFilter() {
SingleSignOutFilter sign = new SingleSignOutFilter();
sign.setIgnoreInitConfiguration(true);
return sign;
}
@Bean
LogoutFilter logoutFilter() {
LogoutFilter filter = new LogoutFilter(casServerProperties.getLogout(), new SecurityContextLogoutHandler());
filter.setFilterProcessesUrl(casClientProperties.getLogoutRelative());
return filter;
}
}
这个配置文件略长,但是并不难,我来和大家挨个解释:
- 首先一进来注入三个对象,这三个中,有两个是我们前面写的配置类的实例,另外一个则是 UserDetailsService,关于 UserDetailsService,我想我也不必多做解释,大家参考本系列前面的文章就知道 UserDetailsService 的作用(Spring Security 如何将用户数据存入数据库?),一会我会给出 UserDetailsService 的实现。
- 接下来配置 ServiceProperties,ServiceProperties 中主要配置一下 Client 的登录地址即可,这个地址就是在 CAS Server 上登录成功后,重定向的地址。
- CasAuthenticationEntryPoint 则是 CAS 验证的入口,这里首先设置 CAS Server 的登录地址,同时将前面的 ServiceProperties 设置进去,这样当它登录成功后,就知道往哪里跳转了。
- TicketValidator 这是配置 ticket 校验地址,CAS Client 拿到 ticket 要去 CAS Server 上校验,默认校验地址是:https://cas.javaboy.org:8443/cas/proxyValidate?ticket=xxx
- CasAuthenticationProvider 主要用来处理 CAS 验证逻辑,关于 AuthenticationProvider 松哥在前面的文章中和大家分享过(SpringSecurity 自定义认证逻辑的两种方式(高级玩法)),当时就说,想要自定义认证逻辑,如短信登录等,都可以通过扩展 AuthenticationProvider 来实现,这里的 CAS 登录当然也不例外,这里虽然设置了一个 userDetailService,但是目的不是为了从数据库中查询数据做校验,因为登录是在 CAS Server 中进行的,这个的作用,我在后面会做介绍。
- CasAuthenticationFilter 则是 CAS 认证的过滤器,过滤器将请求拦截下来之后,交由 CasAuthenticationProvider 来做具体处理。
- SingleSignOutFilter 表示接受 CAS Server 发出的注销请求,所有的注销请求都将从 CAS Client 转发到 CAS Server,CAS Server 处理完后,会通知所有的 CAS Client 注销登录。
- LogoutFilter 则是配置将注销请求转发到 CAS Server。
接下来我再来给大家看下我定义的 UserDetailsService:
@Component
@Primary
public class UserDetailsServiceImpl implements UserDetailsService{
@Override
public UserDetails loadUserByUsername(String s) throws UsernameNotFoundException {
return new User(s, "123", true, true, true, true,
AuthorityUtils.createAuthorityList("ROLE_user"));
}
}
既然是单点登录,也就是用户是在 CAS Server 上登录的,这里的 UserDetailsService 意义在哪里呢?
用户虽然在 CAS Server 上登录,但是,登录成功之后,CAS Client 还是要获取用户的基本信息、角色等,以便做进一步的权限控制,所以,这里的 loadUserByUsername 方法中的参数,实际上就是你从 CAS Server 上登录成功后获取到的用户名,拿着这个用户名,去数据库中查询用户的相关信心并返回,方便 CAS Client 在后续的鉴权中做进一步的使用,这里我为了方便,就没有去数据库中查询了,而是直接创建了一个 User 对象返回。
接下来,我们再来看看 Spring Security 的配置:
@Configuration
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint;
@Autowired
AuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider;
@Autowired
SingleSignOutFilter singleSignOutFilter;
@Autowired
LogoutFilter logoutFilter;
@Autowired
CasAuthenticationFilter casAuthenticationFilter;
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider);
}
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/user/**")
.hasRole("user")
.antMatchers("/login/cas").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.exceptionHandling()
.authenticationEntryPoint(authenticationEntryPoint)
.and()
.addFilter(casAuthenticationFilter)
.addFilterBefore(singleSignOutFilter, CasAuthenticationFilter.class)
.addFilterBefore(logoutFilter, LogoutFilter.class);
}
}
这里的配置就简单很多了:
- 首先配置 authenticationProvider,这个 authenticationProvider 实际上就是一开始配置的 CasAuthenticationProvider。
- 接下来配置
/user/**格式的路径需要有 user 角色才能访问,登录路径/login/cas可以直接访问,剩余接口都是登录成功之后才能访问。 - 最后把 authenticationEntryPoint 配置进来,再把自定义的过滤器加进来,这些都比较容易我就不多说了。
最后,再提供两个测试接口:
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
@GetMapping("/user/hello")
public String user() {
return "user";
}
}
OK ,如此之后,我们的 CAS Client 现在就开发完成了,接下来启动 CAS Client,启动成功后,浏览器输入 http://client1.cas.javaboy.org:8080/user/hello 访问 hello 接口,此时会自动跳转到 CAS Server 上登录,登录成功之后,经过两个重定向,会重新回到 hello 接口。
# 3.小结
OK,这就是松哥和大家介绍的 Spring Security + CAS 单点登录,当然,这个案例中还有很多需要完善的地方,松哥会在后面的文章中继续和大家分享完善的方案。
好了 ,本文就说到这里,本文相关案例我已经上传到 GitHub ,大家可以自行下载:https://github.com/lenve/spring-security-samples
好啦,小伙伴们如果觉得有收获,记得点个在看鼓励下松哥哦~